The Advantages of mmWave Radar Sensors Over PIR Sensors for Lighting Control and Smart Lighting Applications
Energy efficiency is one of the main reasons for investing in a smart lighting system, and choosing the right type of sensor technology will determine its performance. While PIR (passive infrared) sensors have been the go-to solution for lighting control in the past several years, mmWave (millimeter wave) radar sensors are emerging as a powerful alternative that solves the most common PIR sensor shortcomings. We will discuss some of the main reasons to opt for mmWave technology for any kind of smart home or smart office lighting control application.
NOVELIC RIOT100 mmWave human presence detection sensor
More single-sensor features
The only information a PIR sensor can provide is presence detection, without being able to distinguish between a single person or multiple people or between a human or an animal. This provides a discreet ‘empty/occupied’ output with no information on whether the detected target is moving or its position.
mmWave radar sensors can offer multi-modal capabilities by detecting presence, distance from the sensor, and the velocity of the target. This helps ignore false alarms coming from objects with moving parts (air conditioning unit fans, water running through pipes, etc.) since they have velocity but no change in distance. Since mmW sensors detect distance, they can be effectively used to light up different areas as a person is moving through a hallway or a staircase and help significantly reduce energy consumption.
Unaffected by weather or lighting conditions
Possibly the greatest advantage of mmWave radar sensors over competing technologies is that they work reliably in harsh weather conditions like rain or snow, in reduced visibility circumstances like fog or sandstorms, and in all lighting including direct sun glare or complete darkness.
Unaffected by temperature
PIR sensors are sensitive to temperature changes, which can result in false triggers or missed detections when outdoor temperature is close to or above human body temperature. mmWave radar sensors are not influenced by temperature fluctuations, making them ideal for environments where temperature variations are common, such as outdoor or industrial settings. This ensures accurate and dependable motion detection in all operating conditions.
Customizable monitoring areas
With mmWave radar sensors, it is easy to set the limits of the desired monitoring area (for instance: ignore all presence and movement at distances greater than 4 meters from the sensor). Here is an example of where PIR sensors underperform: imagine having an outdoor PIR-based lighting system in someone’s front yard. Since it is very difficult to precisely limit the range of PIR sensors, lights would often get turned on by people or cars passing by in the street. mmWave technology makes it easy to precisely set the detection range.
Increased accuracy
A common disadvantage of PIR sensors for outdoor use is the amount of false triggers coming from inanimate objects like branches moving in the wind, moving shadows, etc. mmWave radar systems aren’t triggered by events like these and thus provide highly accurate motion and presence detection.
Higher motion sensitivity
mmWave radar sensors are able to detect even the slightest movements and gestures, like a person’s heart rate or breathing. Thanks to reliably detecting these so-called micromovements, mmWave radar sensors can tell if a room or any monitored area has been occupied with great accuracy. This solves a very common problem with PIR sensors that will falsely detect that the room is empty and turn the lights off if someone is moving very slowly or is still for a while.
Longer range and more mounting options
mmWave radar sensors offer wider coverage compared to PIR sensors and can cover larger areas, reducing the number of sensors required for comprehensive lighting control. Moreover, mmWave radar sensors provide flexibility in terms of mounting location and positioning, allowing for optimal coverage and customization.
Invisible integration
High-end lighting design requires sensors that won’t visually interrupt the aesthetics, and PIR sensors are bulky and hard to discreetly integrate. One of the great advantages of mmWave sensors is that the radar waves pass through a variety of non-conductive materials like plastics, ceramics, wood, plaster, etc. This way, sensors can be placed inside switches or luminaires without affecting the visual appearance.
No cleaning necessary
If a PIR sensor’s lens gets covered in dust, cobwebs, or any other type of dirt, this will affect its performance. PIR sensors require regular cleaning and maintenance to ensure they work properly. On the other hand, since mmWave signal passes through all sorts of non-conductive materials, you don’t ever need to clean the sensor.
Anonymous monitoring
It is important to point out that both PIRs and mmW sensors provide anonymous detection which is necessary for occupancy detection and lighting control in environments such as public or office restrooms. Due to PIRs being unable to detect slow or small movement, mmWave radars are a great alternative for lighting control in areas that require user privacy.
Final words
With such a wide scope of possible applications, a resistance to weather, lighting, or temperature changes, and superior performance, mmWave radar sensors are a great alternative to PIR. By leveraging the unique capabilities of mmWave technology, lighting systems can provide optimized illumination, improved user experience, and significant energy savings.
NOVELIC offers RIOT100, a mmWave radar sensor for motion and presence detection with a custom detection range of up to 20 meters. To learn more, visit the RIOT100 page, download the RIOT100 brochure, request a datasheet or an evaluation kit, or contact our team for additional questions.
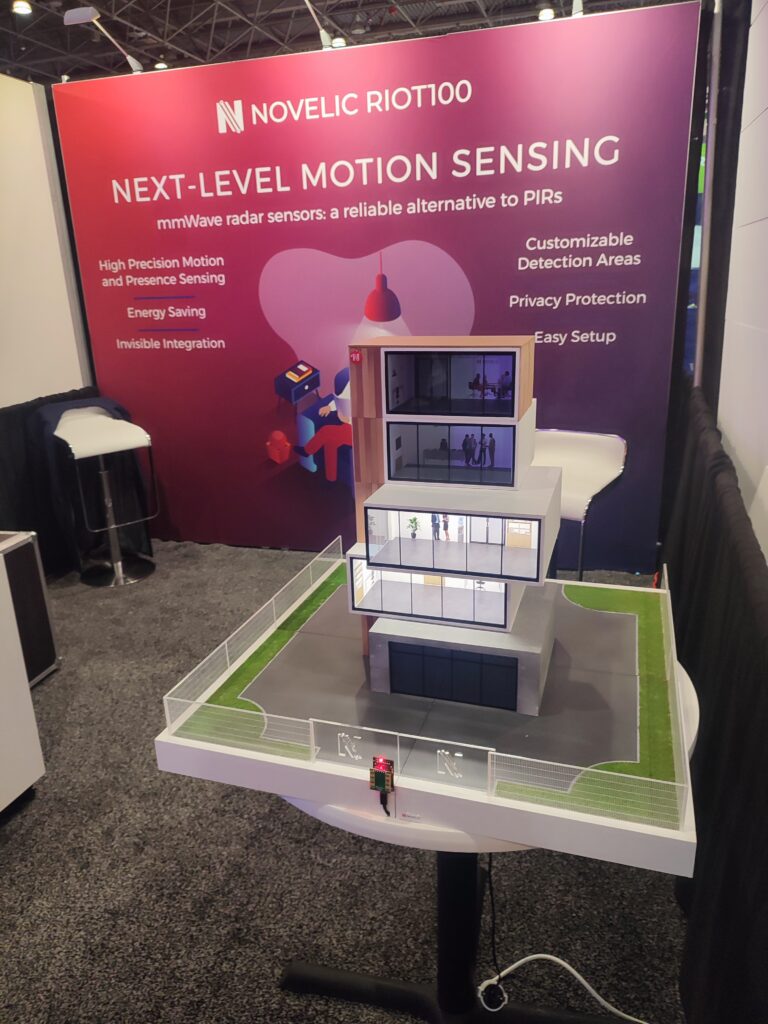

Demo of RIOT100 mmWave sensor being used for smart lighting control
