Sensor Fusion for Automotive and Security Applications
As technology continues to advance, sensor fusion has emerged as a key enabler in various domains, changing the way we perceive and interact with the world around us. From autonomous driving to perimeter security, sensor fusion techniques have proven instrumental in enhancing safety, accuracy, and situational awareness.
In the automotive industry, the race towards fully autonomous vehicles has intensified the need for advanced perception systems that can accurately interpret the surrounding environment. Simultaneously, sensor fusion has transformed the field of security, particularly in perimeter surveillance applications. We will discuss the possible applications of sensor fusion in automotive and security areas and the ways traditional single-sensor systems can be enhanced and improved by real-time, multi-modal information.
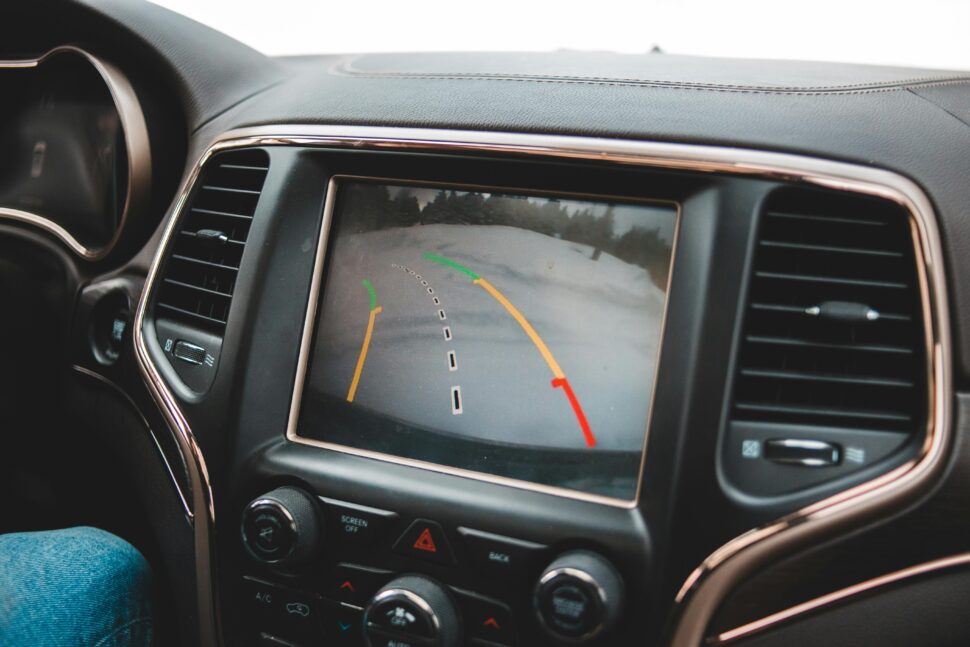

Sensor Fusion for Autonomous Driving
Sensor fusion is a crucial technology in the field of automotive systems, particularly for advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. It involves combining data from various sensors to obtain a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the vehicle’s surroundings. The fusion of sensor data enables the vehicle to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions in real-time.
In automotive applications, sensor fusion typically involves integrating data from different types of sensors such as lidars, radars, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors.
Each sensor has its strengths and weaknesses, and by combining their data, the limitations of individual sensors can be mitigated, resulting in a more robust perception system.
Sensor fusion algorithms employ techniques such as data filtering, calibration, sensor alignment, and data association to accurately merge the information from different sensors.
The fused sensor data is processed by algorithms, such as Kalman filters, particle filters, or deep learning-based methods, to estimate the position, velocity, and orientation of surrounding objects, including vehicles, pedestrians, and obstacles. These estimates are then used by the vehicle’s control systems to make decisions, such as collision avoidance, adaptive cruise control, and lane-keeping.
Sensor fusion in automotive systems is a rapidly evolving field, and ongoing research and development aim to improve the accuracy, reliability, and efficiency of the fusion algorithms. Additionally, the emergence of new sensor technologies, such as solid-state lidar and advanced camera systems, contributes to further advancements in sensor fusion for automotive applications.

Sensor Fusion for Security
Sensor fusion techniques can also be applied to perimeter security systems to enhance their effectiveness in detecting and responding to potential security threats. For example, cameras provide visual information, motion sensors detect movement, and infrared sensors detect heat signatures. Since each sensor provides unique information about the environment, sensor fusion allows the system to leverage multiple modalities, such as visual, acoustic, and thermal data, to create a more comprehensive and robust perception. This multimodal perception helps in detecting different types of threats, such as intruders, vehicles, or even abnormal environmental conditions like fires or gas leaks.
By deploying multiple sensors throughout the perimeter, sensor fusion systems can achieve broader coverage. Each sensor contributes to the overall surveillance network, and fusing their data provides redundancy in case of sensor failures or blind spots. This redundancy enhances the reliability of the system and reduces the risk of missed detections or false negatives. Sensor fusion enables contextual awareness by considering the spatial and temporal relationships between different sensor inputs. By analyzing the combined data, the system can obtain a more complete understanding of the situation, such as the direction of movement, speed, and behavior of detected objects. This contextual information allows security personnel to respond more effectively and make informed decisions in real time.
One of the challenges in perimeter security is dealing with false alarms caused by environmental factors or sensor noise.
Sensor fusion helps mitigate false alarms by cross-validating and correlating information from multiple sensors. For example, a sudden detection by a motion sensor can be verified by the corresponding visual data from cameras, reducing false positives and increasing the reliability of alarm triggers.
Sensor fusion can be integrated with automated response systems, such as security cameras with pan-tilt-zoom capabilities or automated access control systems. When a threat is detected through sensor fusion, the system can trigger appropriate responses, such as activating specific cameras, sounding alarms, or initiating access control measures. This integration enhances the overall security infrastructure and enables rapid and targeted responses to potential threats.
Sensor fusion techniques, coupled with intelligent algorithms and real-time analysis, can significantly enhance the effectiveness of perimeter security systems. By integrating data from multiple sensors and leveraging their respective strengths, sensor fusion contributes to more accurate threat detection, reduced false alarms, and improved situational awareness for perimeter security applications.
The Benefits of Radar and Camera Sensor Fusion
Radar is an excellent choice of technology to pair up with a camera system. Due to these two types of sensors providing different types of information (camera images and the data on the distance, velocity, and angle from the radar), data fusion helps in object detection and classification with greater precision and accuracy.
Complementary Sensing
Radar and cameras have complementary strengths and weaknesses. Radar sensors are great at detecting and tracking objects in poor visibility conditions such as snow, fog, rain, or darkness. On the other hand, cameras offer high-resolution visual information, enabling detailed object recognition such as classifying traffic signs or lane detection. By fusing radar and camera data, the system can leverage the advantages of both sensors, resulting in a more comprehensive and robust perception of the environment.
Improved Object Detection and Tracking
Radar sensors are particularly effective in detecting and tracking objects that might be challenging for cameras, such as vehicles in adjacent lanes or objects hidden by obstacles. The ability of radars to detect velocities and motion patterns enhances the accuracy of object tracking. By combining radar and camera data, the system can improve object detection, tracking, and classification, enabling better situational awareness.
System Redundancy
Sensor redundancy is crucial for safety-critical systems. By fusing radar and camera data, the system gains redundancy in object detection and tracking. In case one sensor fails or encounters limitations, the other sensor can provide supplementary information, reducing the risk of false detections or missed objects. This redundancy improves fault tolerance and system robustness, contributing to a safer environment.
Enhanced Perception Range
Radar sensors excel at detecting and classifying objects at longer ranges, while cameras provide detailed visual information at closer distances. By fusing radar and camera data, the system can extend its perception range, enabling early detection of objects and potential hazards. This enhanced perception contributes to better decision-making and planning, particularly in highway driving or complex urban environments.
Reduced False Positives
Combining radar and camera data allows for improved object confirmation and validation. By cross-referencing the measurements from both sensors, the system can verify the presence and characteristics of detected objects. This validation helps reduce false positives and improves the reliability of object detection and tracking, which is crucial for applications in the automotive industry.
Overcoming Weather and Lighting Challenges
Radar sensors are less affected by environmental factors such as lighting conditions, glare, or harsh weather compared to cameras. By fusing radar and camera data, the system can maintain perception capabilities in various environmental conditions. In challenging scenarios, where one sensor might face limitations, the fusion of data ensures a more reliable perception system.
Conclusion
Sensor fusion is a powerful technology that unlocks a world of possibilities in both automotive and security applications. The integration of data from multiple sensors enhances the overall safety and the decision-making process of the system, paving the way for autonomous vehicles that can navigate complex environments and security systems that can effectively detect and respond to threats. As research and development in sensor fusion continue to advance, we can expect even greater breakthroughs that will shape the future of mobility and security.
Interested in learning more about sensor fusion and its applications? Visit our sensor fusion page and check out all services offered by NOVELIC including sensor calibration, synchronization, and deep learning fusion.
